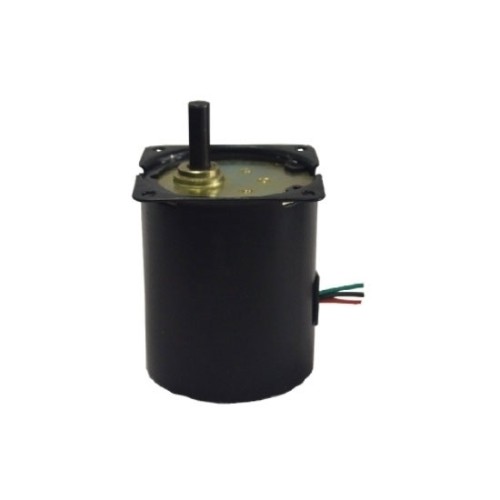

60 rpm AC Synchronous Gear Motor 24V/110V/220V
from
$76.83
Ex Tax: $76.83
- Stock: In Stock
- Model: SCJ009585
- SKU: SCJ009585
Products Sold: 0
Product Views: 715
Available Options
Ask a Question About This Product
- Description
60 rpm AC Synchronous Gear Motor 24V/110V/220V
Brief
AC permanent magnet synchronous gear motor, 1 phase, 60 rpm low output speed at 7/ 10 Kgf•cm output torque, optional voltage 24V/ 110V/ 220V – 240V, 50/ 60Hz, duty type S1 continues or S2 (30 mins). It is compact and CW or CCW rotation at constant speed.
Description
AC PMSM electric motor is mostly used for air cooler, laminator, outdoor auto control machine and monitor, etc. It is reversible and starts by capacitor.
Specification
| Model | SCJ009585 | |||||
| Duty Type | S1 Continues | S2 (30 mins) | ||||
| Voltage (AC) | 24V | 110V | 220V-240V | 24V | 110V | 220V-240V |
| Power Frequency | 50/60 Hz | 50/60 Hz | ||||
| Output Speed | 60 rpm | |||||
| Output Torque | 7 Kgf·cm | 10 Kgf·cm | ||||
| Rated Speed | 1200 rpm | 1200 rpm | ||||
| Input Power | < 17W | < 25W | ||||
| Input Current | < 0.65A | < 0.15A | < 0.08A | < 1.5A | < 0.35A | < 0.2A |
| Rotation | CW/CCW (Reversible) | CW/CCW (Reversible) | ||||
| Operating Temperature | -15 ~ 40℃ | -15 ~ 40℃ | ||||
| Coil Temperature Rise | < 80K | < 80K | ||||
| Insulation Class | B | B | ||||
| Insulation Strength | AC 1500/ 50Hz/min | AC 1500/ 50Hz/min | ||||
| Recommended Capacitance | 47μF/ 63V | 2.2μF/ 250V | 0.56μF/ 450V | 67μF/ 63V | 3.0μF/ 250V | 0.8μF/ 450V |
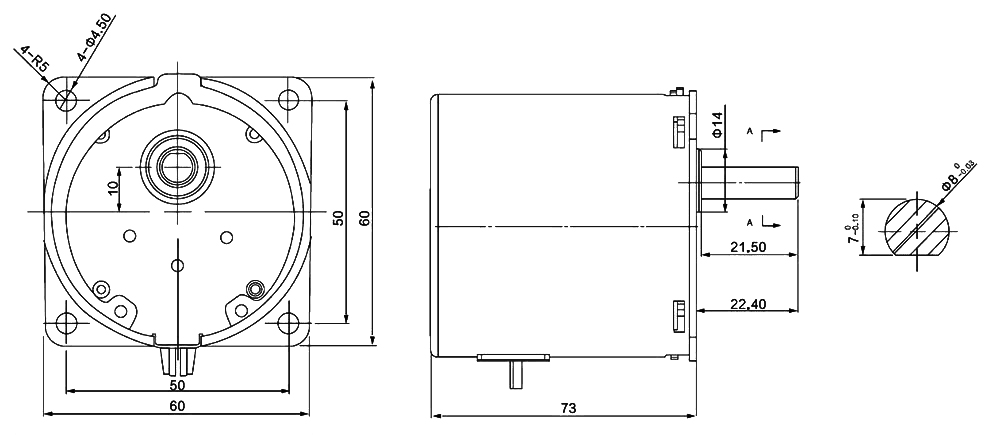
Dimensions (Units: mm)
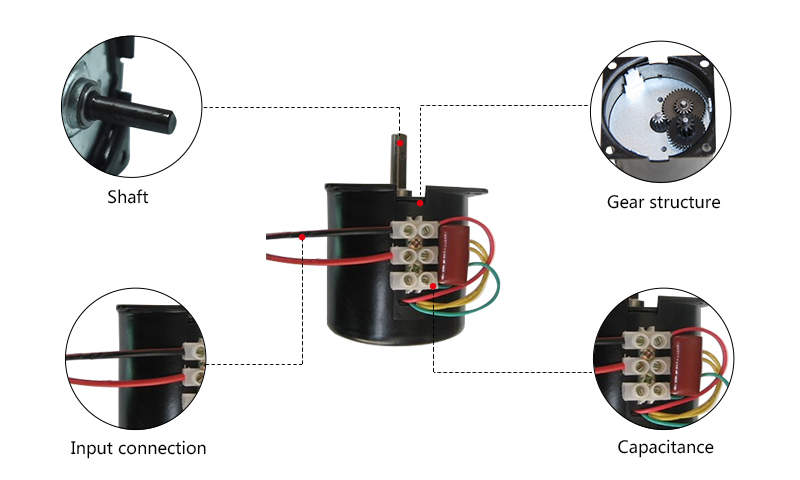
Details
Tips: AC synchronous motor basics
- The speed of a synchronous motor is dependent only on the stator frequency.
- Below the base speed, the stator voltage is proportional to the stator frequency, that is, the higher the motor speed is, the higher the stator voltage and frequency of the motor are, and the current increases with the increase of the speed.
- Above the base speed, the stator voltage only rises to the rated voltage, the stator frequency rises and the rotor current decreases.
- The stator current is proportional to the load, and the rotor current increases with the increase of the load, but not in a proportional relationship, that is, when the stator current increases, the rotor current also increases.
- When the AC synchronous motor is directly connected to the grid, it must be dragged to the synchronous speed by other power before the stator can be connected to the grid. The reason is that when the motor does not rotate, there is no counter electromotive force. If the stator is connected to the grid at this time, it is equivalent to the stator short circuit, which will burn the motor.
- Reviews










