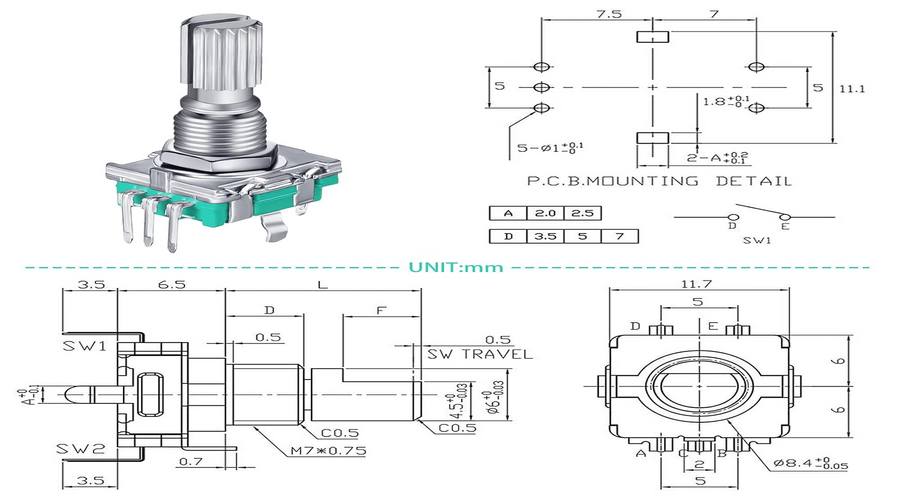
Principles of Rotary Switches
A rotary switch, also known as a selector switch, is a type of electronic mechanical device that allows the user to select between multiple circuits or positions by rotating a knob or handle. The basic principle of a rotary switch lies in its internal construction, which typically consists of a rotor with contacts that align with stationary contacts when the rotor is turned.
The rotor is usually made of an insulating material with conductive segments or contacts embedded within it. As the rotor rotates, these contacts make or break electrical connections with the stationary contacts, thus switching the circuit. The number of positions or circuits that can be selected depends on the design of the switch, with common configurations ranging from 2 to 12 positions.
Types of Rotary Switches
Rotary switches come in various forms, each tailored to specific applications. Some of the most common types include:
- Single-Pole, Single-Throw (SPST): The simplest type, which connects or disconnects a single circuit.
- Single-Pole, Double-Throw (SPDT): Allows selection between two circuits.
- Double-Pole, Double-Throw (DPDT): Provides independent control of two circuits, often used in applications requiring reversing polarity.
- Multi-Pole, Multi-Throw (MPMT): Capable of controlling multiple circuits simultaneously, suitable for complex systems.
Applications of Rotary Switches
The versatility of rotary switches makes them indispensable in a wide range of applications. Here are some notable examples:
Audio Equipment: In audio systems, rotary switches are used to select different input sources, such as microphones, turntables, or auxiliary devices. They also control functions like volume, tone, and balance.
Automotive Industry: Rotary switches are used in vehicles to control various functions, including headlights, windshield wipers, and fan speeds. They offer a robust and intuitive interface for drivers.
Industrial Machinery: In industrial settings, rotary switches are employed to control the operation of machinery, select between different modes of operation, or adjust parameters like speed and temperature.
Home Appliances: From washing machines to ovens, rotary switches are used to set programs, control temperatures, and select functions in various household appliances.
Lighting Control: In lighting systems, rotary switches can be used to dim lights, switch between different lighting circuits, or control the color and brightness of LED lights.
Advantages of Rotary Switches
- Durability: Rotary switches are known for their robust construction and long lifespan, making them suitable for harsh environments.
- Simplicity: Their straightforward design and easy operation make them accessible to users of all ages and skill levels.
- Versatility: The ability to control multiple circuits with a single device reduces the need for multiple switches, simplifying wiring and installation.
- Reliability: Rotary switches provide a tactile feedback that reassures users of the switch's position, reducing the risk of accidental operation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, rotary switches are a fundamental component in many electrical and electronic systems, offering a reliable and user-friendly way to control circuits and functions. Their versatility, durability, and simplicity make them an ideal choice for a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to industrial machinery. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the design and capabilities of rotary switches, ensuring they remain a vital part of our electrical landscape for years to come.











Leave a comment