
- Stock: In Stock
- Model: SCJ009488
- SKU: SCJ009488
Ask a Question About This Product
- Description
1 hp (0.75kW) Induction Motor 3 phase 4 pole AC Induction Motor
Brief
Description
1 hp (0.75kW) 3-phase 4-pole AC induction electric motor is widely used in various kinds of general purpose machineries like fans, pumps, compressors, machine tools, gearboxes, transportation and so on. Low cost and manufacturer direct sale.
1hp Induction Motor Specification
| Basics | Model | SCJ009488 | ||
| Design Standard | IEC | |||
| Weight | 15kg | |||
| Frame Type | 80M | |||
| Mounting | Horizontal Foot Mounting (B3) | |||
| Wiring Method | Output≤4hp (3kW), Y connection Output≥5.5hp (4kW), Delta connection | |||
| Degree of protection | IP54/IP55 | |||
| Insulation Class | Class F | |||
| Cooling | TEFC(compliance to IC 411 code of IEC 60034-6) | |||
| Technical Parameters | Nominal Output | 1hp or 0.75kW | ||
| Pole Number | 4-pole | |||
| Nominal Speed | 1390rpm | |||
| Frequency | 50Hz | |||
| Nominal Voltage | 380V (Y connection by default) / 220V (Change Y to Δ connection on your own) | |||
| Nominal Current (full load) | 2.05A/3.55A | |||
| Efficiency | 73% | |||
| Power Factor( cosφ) | 0.76 | |||
| Nominal Torque (Tn) | 5.15Nm | |||
| Locked Rotor Torque/Nominal Torque (TST/Tn) | 2.3 | |||
| Maximum Torque/Nominal Torque (Tmax/Tn) | 2.3 | |||
| Locked Rotor Current/Nominal Current (IST/In) | 6.0 | |||
| Noise Level | 58dB/(A) | |||
| Environment | Ambient Temperature | -15℃+40℃ | ||
| Altitude | Less than 1000m above sea level | |||
3-phase Induction Motor Dimensions
| Frame Type | Mounting Dimensions (mm) | Overall Dimensions | |||||||||||||
| A | A/2 | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | K | AB | AC | AD | HD | L | |
| 80M | 125 | 62.5 | 100 | 50 | 19 | 40 | 6 | 15.5 | 80 | 10 | 165 | 175 | 145 | 220 | 295 |
Wiring Diagrams (Three-phase squirrel-cage induction motor)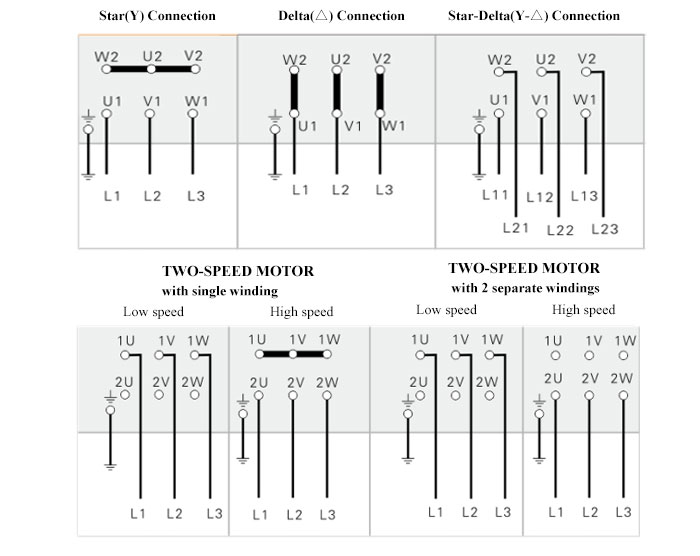
Details

Tips: What is an induction motor or asynchronous motor?
An induction motor or asynchronous motor is an AC electric motor. When the induction motor running, there is relative motion between the rotating magnetic field and rotor windings in the air gap, and the induction current in the rotor windings under the effect of electromagnetic induction produces the electromagnetic torque, so as to achieve the conversion of electrical and mechanical energy.
The stator of the induction motor is not the rotational part of motor, and its main task is to produce a rotating magnetic field. The rotating magnetic field is not achieved by the mechanical method, but by means of that the AC in the several pairs of electromagnets makes the nature of the magnetic pole change circularly, which is equivalent to a rotating magnetic field. The rotor is a rotatable conductor, mostly showing the shape of squirrel caged. Rotor winding is divided into two types of squirrel-cage and wound.
Under normal circumstances, the rotor speed of the induction motor is always slightly lower than the speed of the rotating magnetic field (synchronous speed), so the induction motor is also known as the asynchronous motor.
Documents
3-Phase Induction Motor (IEC) Catalog.pdf
- Reviews














