





- Stock: In Stock
- Model: SCJ009602
- SKU: SCJ009602
Available Options
Ask a Question About This Product
- Description
1/6 hp Piston Air Motor 1000 rpm 211 L/min
Brief
Description
piston air motor with starting torque 1 Nm, stopping torque 1.7 Nm, 1:1 gear ratio. The pneumatic piston motor is mainly used in mining machinery, and it can be used as drive motors for conveyor belts, etc.
Specification
| Model | SCJ009602 |
| Power | 1/6 hp |
| Gear ratio | 1:1 |
| Rated speed | 1000 rpm |
| Rated torque | 0.84 Nm |
| Max. no-load speed | 2000 rpm |
| Air consumption | 211 L/min |
| Starting torque | 1 Nm |
| Stopping torque | 1.7 Nm |
| Mounting type | Basic type/ flange type/ foot type |
| Certificate | CE |
| Warranty | 12 months |
Dimension
Basic type

Flange type
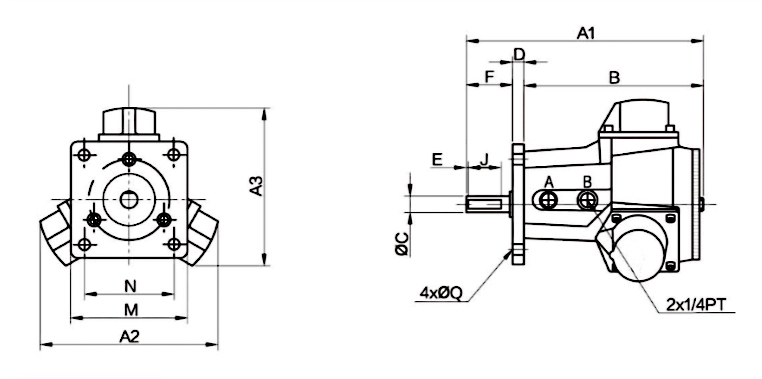
Foot type

| Model | Dimension (mm) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | B | C | C1 | D | E | F | G | H | J | M | N | M1 | N1 | M2 | N2 | Q | Q1 | P | |
| SCJ009602 | 168 | 135 | 122 | 140 | 126 | 12 | 55 | 10 | 2 | 32 | M5 | 42h7 | 25 | 74 | 57 | 100 | 70 | 50 | 30 | 7 | 9 | 71 |
Details
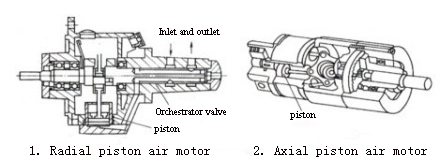
Tips: Working Principle of Piston Air Motor.
The schematic diagram of the structure of a piston type air motor is a pneumatic motor that converts the linear motion of several pistons into a rotary motion through a crank or a swash plate. Its structure has two kinds of radial piston type and axial piston type.
Figure 1 shows the structural principle of the most common radial piston air motor. The working chamber is composed of pistons and cylinders. Three to six cylinders are distributed radially around the crankshaft, and each cylinder is connected to the crankshaft through a connecting rod. The compressed air distribution valve supplies air to each cylinder in sequence, and the compressed air pushes the piston to move and drives the crankshaft to rotate. When the valve is turned to a certain angle, the remaining air in the cylinder is discharged through the exhaust port. Changing the direction of intake and exhaust can realize the forward and reverse conversion of the air motor.
Figure 2 shows the structural principle of an axial piston air motor. Cylinders are evenly distributed in the axial direction. The pistons of the cylinders make reciprocating linear motions in turn under the action of the input compressed air, and the linear motion is transformed into the rotary motion of the output shaft through the action of the swash plate.
- Reviews



















